ASKA – Skeletal Striated Muscle Antibody:
Why ASMA – Anti Skeletal Striated Muscle Antibody Test?
CLINICAL INFORMATION
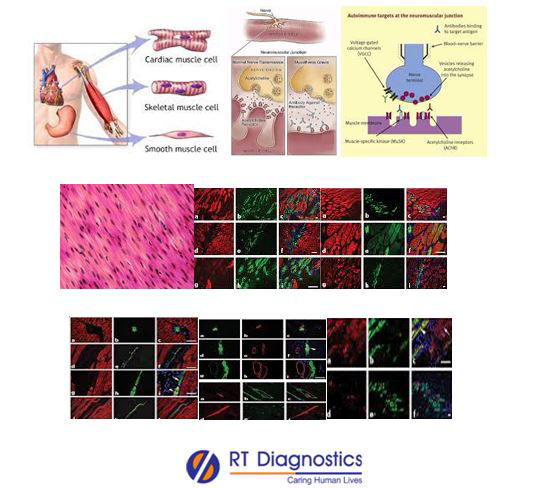
The muscle is soft tissue. There are about 600 muscles in the human body. Three main types of muscles are skeletal, smooth muscle and cardiac muscles. Skeletal muscles belong to the muscular system. They contributes 30 to 40 % of total body mass and its function is to enhance mobility since they are voluntary in action (the neuro-muscular system involves the brain, nerve and skeletal muscles). Skeletal muscles connect to the bones and thus allow them to perform a wide range of movements. Striated muscle is composed of a linear array of multinucleated muscle fibres. This tissue consists of repeating functional units called as sarcomeres. Pathologies associated with its pathology include neurogenic atrophy, muscular dystrophies, congenital myopathies, inflammatory myopathies, toxic myopathies, diseases of a neuromuscular junction etc. Symptoms of muscle disorders include weakness, abnormal fatigue with activity, muscle spasms, and muscle twitching. Clinical manifestations of neuromuscular disorders include drooping eyelids, double vision, slurred speech, difficulty swallowing, difficulty breathing etc. Anti-striated muscle (anti-SM) antibody refers to a class of antibodies against components of skeletal muscles such as alpha-actin, myosin, titin, ryanodine etc. Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune neurological disease characterized by muscle fatigue and inactivity primarily in the voluntary muscles. These antibodies block the receptor sites of acetylcholine (a major neurologic transmitter). Clinical features of MG includes chronic fatigue, droopy eyelids, delayed muscle response, slow chewing etc. Striated skeletal muscle antibodies are found in patients with Myasthenia gravis - MG (the most striking characteristic feature for the presence of anti-acetylcholine receptor antibodies – AchR, which are the hallmark features of MG), but the presence of striated muscle antibodies in MG strongly suggests the association of pathology such as thymoma (anti-titin antibodies are sensitive markers of thymoma associated with MG). The presence of IgM anti-striated muscle antibodies are tested positive in patients with nuclear hepatitis, infectious hepatitis, acute viral infections, polymyositis, EBV etc. Another related condition of extremely elevated anti-striated muscle antibodies is granulomatous myositis - GM (a rare disease that predominantly results in proximal or rarely even distal muscle weakness in the upper and/or lower extremities) with the absence of MG. Multinucleated giant cells is the hallmark of Non- Caseating granuloma formation. Granulomatous myositis (GM) is found to be associated with sarcoidosis, thymoma/Myasthenia gravis, Crohn’s disease, tuberculosis, brucellosis, lymphoma, and syphilis, primary biliary cirrhosis, Wegener’s granulomatosis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic sclerosis etc. Additional tests include electromyography (used to diagnose muscle disorders). Other tests include LDH, imaging studies etc.
General Instructions:
Sample Requirement: Specimen - Blood sample collected from the vein. Test Preparation: None.
NOTE - Sample for specimen collections may vary based on the patient’s condition/cases according to the patient’s presenting complaints/signs or symptoms:
SPECIMEN REQUIREMENT (Special or Rare Cases) - As instructed and guided by Physician / Clinician / Pathologist / as per Laboratory’s requirements, according to procedures and protocols.
This Multi-Specialty Clinical Referral Laboratory RT DIAGNOSTICS provides precise and accurate tests with an extensive range of testing services to the medical centres to help in the diagnosis and identification of pathology in the test specimens for infectious diseases and also to evaluate the function of organ systems of the patient. It prevents further complications and helps to stabilize and restore health to near normalcy at the earliest without delay.



