Protein-S-Activity:
Why Protein-S Activity Test?
CLINICAL INFORMATION
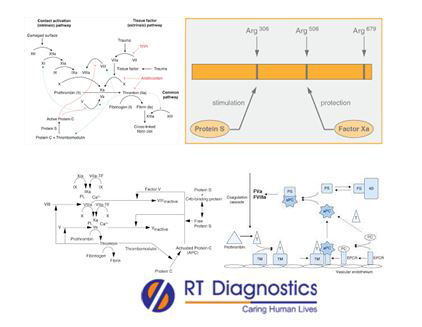
Protein-S (PS) is a vitamin K dependent plasma protein. Protein-S acts as a principal cofactor to protein-C. Hence this cofactor Protein-S enhances the APC thereby inactivating blood clotting factor V and factor VIII. Both protein C and protein S work together to prevent excessive blood clots. Hence deficiency of Protein-S leads to an increased risk of VTE. Deficiency or dysfunctional protein S may be due to liver diseases, kidney disorders, severe infections, cancers etc. Protein S activity test is ordered to study their activity for either excessive blood clotting, to evaluate their ability to regulate and slow down blood clotting, in prognosis (to monitor blood clotting) etc. Measurement of Protein-S – it is based on Protein-S in plasma and free functional Protein-S. It estimates the portion bound to complement protein, C4b-binding protein (C4b BP). Protein-S activity assay - Protein-S levels are hard to ascertain as Protein-S is being a cofactor for the activated protein-C (APC) pathway since it binds to C4b BP, and hence Protein-S activity assay is determined using a clotting based test to measure the cofactor activity. The amount of Protein-S activity is proportional to the clotting value. Some factors that can underestimate the Protein-S levels in plasma include increased levels of factor VIII and factor VLeiden. While a few factors such as lupus anticoagulant has a modulatory effect (i.e can either reflect abnormal results eg. lower or higher values). Moreover, the unbound (free) portion of PS activity can be measured by free PS assay. Factors that lower the PS activity levels include pregnancy, OCPs, inflammation, HRT, certain medications and other acquired causes. Other associated tests include PS antigen assay (based on ELISA or latex particle turbidimetric method are estimated in both free and bound form), which determines the presence of Protein-S and the assay is not based on the Protein-S function. Therefore these test results are extremely helpful in certain blood clotting pathologies such as hyper-coagulable or consumptive states etc. Additional tests include chromogen (amidolytic) based assay – the formation of chromogenic colour is proportional to the amount of activity in the plasma sample specimen (test results can be interfered with by hemolysis, lipemia, icterus etc), antithrombin, lupus anticoagulant, antiphospholipid antibodies, factor VLeiden test, prothrombin test etc. Other tests include CBC, differential count, Peripheral blood smear test for platelets count and thrombocyte activity tests, D-dimer, homocysteine etc.
General Instructions:
Sample Requirement: Specimen - Blood sample collected from the vein. Test Preparation: None.
NOTE - Sample for specimen collections may vary based on the patient’s condition/cases according to the patient’s presenting complaints/signs or symptoms:
SPECIMEN REQUIREMENT (Special or Rare Cases) - As instructed and guided by Physician / Clinician / Pathologist / as per Laboratory’s requirements, according to procedures and protocols.
This Multi-Specialty Clinical Referral Laboratory RT DIAGNOSTICS provides precise and accurate tests with an extensive range of testing services to the medical centres to help in the diagnosis and identification of pathology in the test specimens for infectious diseases and also to evaluate the function of organ systems of the patient. It prevents further complications and helps to stabilize and restore health to near normalcy at the earliest without delay.



