Why Gram Stain (Ascitic Fluid) Test?
CLINICAL INFORMATION
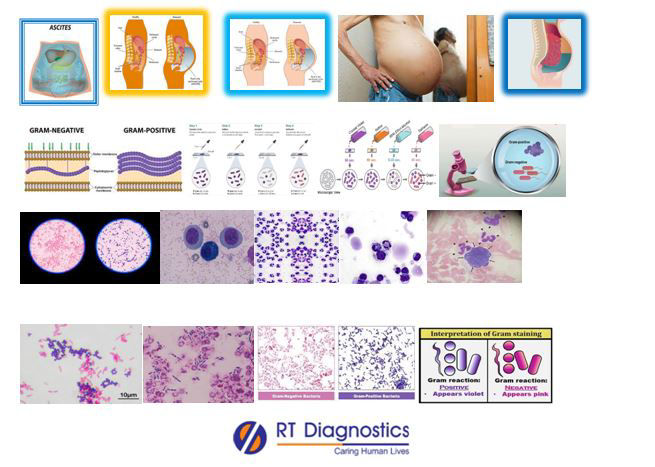
Ascitic Fluid is found in certain diseases and many infections eg. TB and chronic diseases such as liver cirrhosis cause accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity. Thus ascitic fluid accumulated in the cavity in certain pathologies can get infected and can lead to Ascites. An ascitic Fluid test is done to detect peritonitis. Hence peritoneal fluid analysis is used to help diagnose the cause (Transudate or exudate) of fluid build-up in the abdomen (ascites) peritonitis. Transudate and Exudate -This test detects the cause of effusion (such as infection due to bacteria, virus, fungi etc, or non-infectious / inflammatory condition causing peritonitis eg. Congestive heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, hepatic cirrhosis, pancreatitis, ruptured gall bladder, rupture of the appendix, autoimmune diseases etc – Transudate or Exudate) of fluid accumulated in the peritoneal cavity and sometimes around the internal organs. High attenuation of ascites in abdominal ultrasound is thought to be due to high protein and cellular content. Peritonitis is a medical emergency and if untreated by neglect the infection from the peritoneum can spread throughout the body known as sepsis which is a life-threatening condition that consequently leads to shock, organ failure and eventually death. Signs of peritonitis include abdominal pain or tenderness, bloating or feeling of fullness in the abdomen, fever, nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, low urine output and thirst. Other tests for ascites performed are clinically based for ascetic fluid are by inspection for bulging flanks, auscultation. Followed by clinical examination by palpation, flank dullness, shifting dullness etc., for performing ascetic tap. Complications of untreated or chronic ascites include spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (a life threatening infection), blood sepsis, migration of fluid into lung cavities, hepato-renal syndrome, weight loss and protein malnutrition, mental confusion, altered consciousness. Change in level of alertness and/or COMA (hepatic-encephalopathy). Gram stain also called as Gram stain method used for staining to classify two groups of bacterial species such as gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. This term Gram stain is derived from the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram who developed this technique. Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the physical and chemical properties of the bacterial cell wall. Bacteria with gram-positive cell walls have thick peptidoglycan which retains the primary stain crystal violet and Lugol’s iodine solution is added to strengthen the bonds of the stain. While the gram-negative bacteria since they have a thinner bacterial cell wall allow the crystal violet to wash out on the addition of ethanol, hence their cell membrane is stained pink or red by the counterstain (safranin or fuchsine). Other tests for confirmation of ascites include ultrasound and imaging studies like X-Rays, MRI, CT Scan etc, and systematic clinical examination procedures such as inspection, auscultation, percussion, palpation and scratch test are performed for bulging flanks, flank dullness, shifting dullness, fluid wave, puddle sign etc, are tested (High attenuation of ascites in abdominal ultrasound is thought to be due to high protein and cellular content) and elevated jugular venous pressure is also checked and further biochemical investigations such as liver function tests (to check impaired liver function), coagulation tests etc. The identification of the infectious causative agent is thus identified (eg. Gram-positive or Gram-negative) to arrive at a definite diagnosis for starting effective medication (such as broad-spectrum or narrow-spectrum antibiotics) against it. Additional tests include ESR, CRP, D-dimer etc.
General Instructions:
Sample Requirement: Specimen – Ascitic Fluid. Test Preparation: None.
NOTE - Sample for specimen collections may vary based on the patient’s condition/cases according to the patient’s presenting complaints/signs or symptoms:
SPECIMEN REQUIREMENT (Special or Rare Cases) - As instructed and guided by Physician / Clinician / Pathologist / as per Laboratory’s requirements, according to procedures and protocols.
This Multi-Specialty Clinical Referral Laboratory RT DIAGNOSTICS provides precise and accurate tests with an extensive range of testing services to the medical centres to help in the diagnosis and identification of pathology in the test specimens for infectious diseases and also to evaluate the function of organ systems of the patient. It prevents further complications and helps to stabilize and restore health to near normalcy at the earliest without delay.



