Free PSA:
Why Free PSA Test is done?
CLINICAL INFORMATION
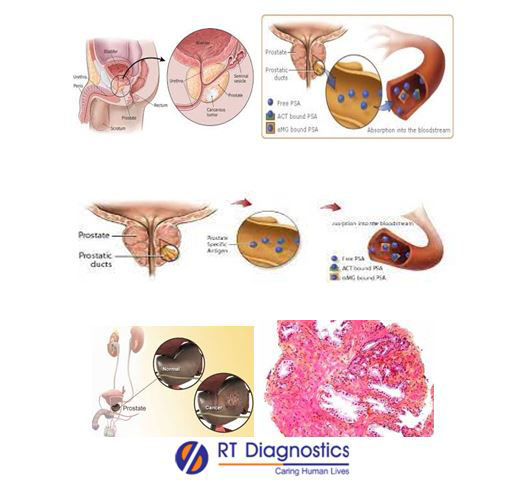
The prostate is a small gland (accessory reproductive organ) situated below the bladder in males. PSA is a prostate-specific antigen – a protein, synthesized by the prostate gland and is released along with the semen. A small quantity of PSA is also found circulating in the blood. There are two types of PSA- Free PSA and PSA in bound form with other proteins (Bound-PSA). Usually, the PSA levels are low in the body. Certain pathologies of the prostate can increase PSA levels, like prostatitis (inflamed prostate), enlarged prostate – BPH etc. PSA Test indicates both the levels of free and bound PSA, while the free PSA test reveals the percentage of unbound PSA (higher PSA levels correlate to lower free PSA levels – inversely proportional). PSA Test measures the PSA in the blood and is a useful diagnostic tool – as a prostatic tumour marker, in the screening (indicates the risk eg. Doubling - The faster the levels of PSA doubles it indicates the aggressive nature) of prostate cancer. Symptoms of prostate cancer include pain during ejaculation, pain in the lower back, frequent urination, painful or burning sensation while urination, bone pain, loss of appetite and weight loss. Risk factors of prostate cancer include age, family history, smoking, alcoholism etc. PSA is found to be varied (fluctuate) in certain conditions such as BPH, prostatitis, UTI, ejaculation, medications, prostate surgery etc. Some of the limitations of the PSA test are misleading results, variations such as (PSA raising factors / PSA lowering factors, PSA density, PSA velocity etc). Other additional tests include Digital rectal examination, rectal prostatic ultrasonography, TRUS – Transrectal ultrasound, cystoscopy – bladder examination etc.
General Instructions:
Sample Requirement: Specimen - Blood sample collected from the vein. Test Preparation: Suggestions from the doctor.
NOTE - Sample for specimen collections may vary based on the patient’s condition/cases according to the patient’s presenting complaints/signs or symptoms:
SPECIMEN REQUIREMENT (Special or Rare Cases) - As instructed and guided by Physician / Clinician / Pathologist / as per Laboratory’s requirements, according to procedures and protocols.
This Multi-Specialty Clinical Referral Laboratory RTDIAGNOSTICS provides precise and accurate tests with an extensive range of testing services to the medical centres to help in the diagnosis and identification of pathology in the test specimens for infectious diseases and also to evaluate the function of organ systems of the patient. It prevents further complications and helps to stabilize and restore health to near normalcy at the earliest without delay.



