Cryoglobulins:
Why Cryoglobulins Test?
CLINICAL INFORMATION
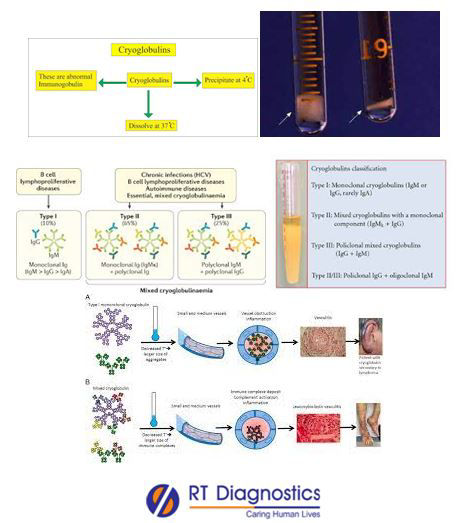
Cryoglobulins are antibody proteins that are found in the blood in certain pathologies like SLE, RA, leukemia, lymphoma, etc. Cryoglobulins are immunoglobulins present in the bloodstream that precipitates when cooled below 37°C and dissolve upon re-warming. These antibodies clump together in the cold and thus may cause inflammation (vasculitis) or organ damage. In a few cases, the level of these antibodies (cryoglobulins) may be low in the blood, without manifesting any clinical signs or symptoms in the body. Cryoglobulinemia is a medical condition in which the blood contains large amounts of antibodies eg. pathological cold-sensitive antibodies in the body. Majority of cryoglobulinemia are secondary manifestations of another disease (any underlying pathology). Complications of cryoglobulins include gelatinous protein clumps of antibodies that can impede blood circulation which can damage skin, joints, nerves, and organs (particularly kidney and liver). Cryoglobulin test is the most neglected but also serves as a useful tool that helps to detect the presence of abnormal proteins i.e antibodies (qualitative) and also for the relative quantity of antibodies in the body in any suspected infection/disease conditions. Some of the diseases associated with cryoglobulins are hepatitis – C, HIV, multiple myloma, Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia, lupus, Sjogren’s syndrome, certain lymphoproliferative disorders (i.e consists of Type-1 cryoglobulins composed of monoclonal immunoglobulins), lymphoma, multiple myloma, etc. Hence this test is ordered along with other tests to help determine a diagnosis and/or for differential diagnosis - to rule out potential causes of cryoglobulinemia. Usually, this condition remains asymptomatic, while in some cases the clinical manifestations include fatigue, joint pain, numbness, weakness, purpura (red rashes/spots/bruises) usually over the lower extremities, Raynaud’s phenomenon bluish discoloration – cyanosis, weight loss, high blood pressure, swelling of ankle and legs, skin ulcer, peripheral neuropathy, gangrene, enlarged liver and/or spleen, kidney damage, numbness or tingling sensation or weakness of hands and/or feet, etc. Additional tests depend upon further investigations based upon its degree of damage, associated organ damage, presence of any other associated disease/disorders (co-morbid conditions), and/or medical conditions. Advanced cryoglobulin testing for the presence of circulating antibodies includes – Type-1: characterized by monoclonal immunoglobulins, Type-II: monoclonal heavy chain, along an associated light chain and polyclonal immunoglobulins, Type-III: only trace amounts of polyclonal immunoglobulins may be present. Other tests include CRP, ESR, serum electrophoresis, Rheumatoid factor in RA, complementary deficiency (AH50, CH50, individual complement testing), connective tissue disorders (i.e ANA-TEST) antinuclear antibody tests, antibodies to DNA, autoimmune hepatitis (anti-mitochondrial antibodies), antibodies to phospholipids, ANCA associated vasculitis i.e anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, viral testing – hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HIV, a skin biopsy (to check for immunoglobulin deposition and/or small cell vasculitis), bone marrow biopsy (to rule out malignancy), monitoring for complications associated predominantly with mixed crypglobulinemia i.e for eg. chronic hepatitis with cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (monitor transaminases, alfa fetoprotein, and liver ultrasound), glomerulonephritis (urinalysis, BUN, BUN/Creatinine, etc), thyroid disease (TSH, antibody testing), skin ulcers (consider arterial/venous Doppler evaluations; repeat testing for vasculitis), etc.
General Instructions:
Sample Requirement: Specimen - Blood sample collected from the vein. Test Preparation: Fasting for 8 hours.
NOTE - Sample for specimen collections may vary based on the patient’s condition/cases according to the patient’s presenting complaints/signs or symptoms:
SPECIMEN REQUIREMENT (Special or Rare Cases) - As instructed and guided by Physician / Clinician / Pathologist / as per Laboratory’s requirements, according to procedures and protocols.
Sample Requirement: Blood Sample taken from the vein
Test Preparation: Fasting for 8 Hours
This Multi-Specialty Clinical Referral Laboratory RT DIAGNOSTICS provides precise and accurate tests with an extensive range of testing services to the medical centers to help in the diagnosis and identification of pathology in the test specimens for infectious diseases and also to evaluate the function of organ systems of the patient. It prevents further complications and helps to stabilize and restore health to near normalcy at the earliest without delay.



