Why Chloride synovial fluid test?
CLINICAL INFORMATION
Chloride is one of the most important electrolytes (other than sodium, potassium, bicarbonates) in the human system that helps to maintain electrical neutrality at the cellular level (by moving into or out of the cells as needed). Electrolytes are electrically charged minerals that regulate the fluid volume and electrolyte balance (of acid-bases – pH balance) in the body and monitor treatment (prognosis – effectiveness of treatment). It helps to maintain fluid homeostasis inside and outside the cells and thus regulates blood volume, blood pressure, and pH of body fluids. Symptoms that may indicate electrolyte (chloride) imbalance include excessive fatigue, muscle weakness, breathing difficulties, frequent vomiting, prolonged diarrhea, excessive thirst, and high blood pressure. Chloride Test helps measure the level of chloride in blood or urine, hence is ordered as a part of electrolyte panel or basic metabolic panel or during routine health check-up and also in some pathological conditions (abnormal levels of chloride). The main source of chloride for the body is food intake (consumption of food) and table salt. Most chloride is absorbed by the digestive tract and excess is eliminated in urine. Symptoms of low chloride (hyperchloremia) include fluid loss, dehydration, weakness or fatigue, difficulty in breathing (respiratory distress such as hyperventilation caused by respiratory alkalosis) diarrhea, and/or vomiting. Excessive secretion of certain hormones such as cortisol and aldosterone can also contribute to body fluid loss (leading to chloride depletion). Other causes of chloride imbalance include congestive heart failure, diabetic ketoacidosis, aldosterone deficiency, prolonged vomiting or gastric suction, Addison disease, emphysema, malabsorption syndrome, primary aldosteronism, chronic lung diseases can lead to respiratory acidosis and/or loss of acid from the body (Metabolic acidosis), etc. Symptoms of high chlorine (hyperchloremia) include kidney failure or kidney disorders, High levels of blood sodium, Cushing syndrome, diabetes insipidus and/or diabetic coma, loss of body fluids from prolonged vomiting, sweating or high fever (dehydration), drugs like NSAIDs, Hormones (androgen, corticosteroids, estrogens) and certain diuretics, etc. Chlorine test is ordered as a part of electrolyte panel (sodium, potassium, chlorine, bicarbonates) in certain conditions such as kidney diseases, heart failure, liver diseases and high blood pressure, etc that leads to an imbalance of fluids in the body. Other tests such as blood gases may also be ordered to further evaluate the severity and cause of extreme imbalance (acidosis or alkalosis). Synovial fluid analysis is also known as joint fluid analysis may be ordered to help diagnose the cause of joint inflammation, pain, swelling, and fluid accumulation. The function of the synovial fluid is to supply nutrition and disposal of metabolic end products, lubricate the joints and absorb shock. Diseases associated with synovial fluid are of two types inflammatory type and non-inflammatory type. Some of the diseases are an auto-immune disease that leads to chronic synovitis (inflammation of synovial membrane), degenerative osteoarthritis (synovial fluid becomes less viscous and inflammatory substances come into direct contact with sensory nerve cells in the joints producing pain), rheumatoid arthritis, gout, tubercular arthritis (mycobacterium tuberculi – acid-fast bacilli), pyogenic arthritis or septic arthritis (increased amount of lactate accumulation), systemic lupus erythematosis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, etc. Chloride synovial fluid test helps
in analysis of any pathology (eg. To know the nature of pathology -Transudate / Exudate) in the specimen, checks for changes in the physical properties like color, viscosity, and screens for changes in the fluid’s biochemical composition, etc. Determination of inflammatory infiltrate is detected by adding acetic acid to the synovial fluid specimen. If a mucin clot is formed it shows the presence of inflammatory cells. Estimation of lactate levels in septic arthritis. Usual routine microscopic analysis is done to detect the presence of monosodium urate crystals (gout), calcium phosphate (pseudo-gout), corticosteroid crystals, and hydroxyl apatite crystals (detected by alizarin red stain), smear study in the synovial fluid specimen for detection of acid-fast mycobacterium bacilli. Typical symptomatic clinical presentation includes pain, stiffness, swelling, cracking sound (since synovial fluid level reduces to fill the expanding volume of the joints negative pressure is formed and carbon-di-oxide gets filled up in the space and this bubble formation is called as cavitation leading to crackling sound), etc, hence this test helps to monitor Acid-Base Balance and during prognosis. Other tests include imaging studies like X-rays etc.
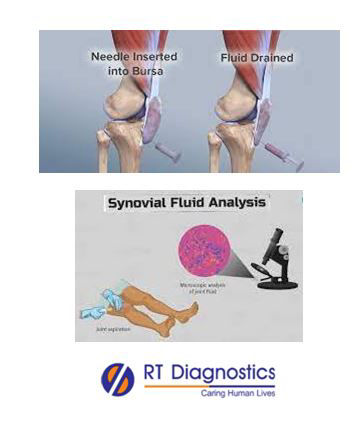
General Instructions:
Sample Requirement: Specimen - Synovial fluid. Test Preparation: None.
NOTE - Sample for specimen collections may vary based on the patient’s condition/cases according to the patient’s presenting complaints/signs or symptoms:
SPECIMEN REQUIREMENT (Special or Rare Cases) - As instructed and guided by Physician / Clinician / Pathologist / as per Laboratory’s requirements, according to procedures and protocols.
Sample Requirement: Synovial fluid
Test Preparation: None
This Multi-Specialty Clinical Referral Laboratory RT DIAGNOSTICS provides precise and accurate tests with an extensive range of testing services to the medical centers to help in the diagnosis and identification of pathology in the test specimens for infectious diseases and also to evaluate the function of organ systems of the patient. It prevents further complications and helps to stabilize and restore health to near normalcy at the earliest without delay.



