Blood Sugar – Post Lunch:
Why Blood Sugar – Post Lunch test?
CLINICAL INFORMATION :
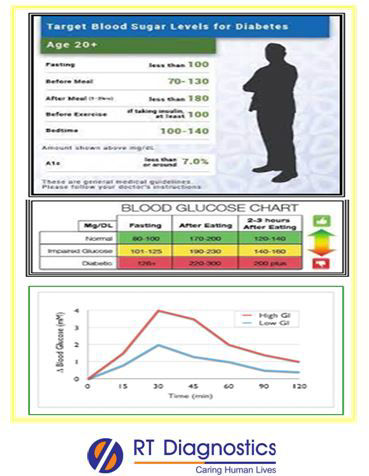
Blood Sugar – Post Lunch test (postprandial blood glucose estimation)is done, approximately 2 hours within/after a meal (lunch/brunch) also called as Post Prandial Blood Sugar Test (PPBS). The test is performed to check how the patient’s body responds after a meal as the blood glucose (the primary source of energy) rises sharply. Hence blood samples are collected every half an hour for two hours for blood glucose levels and the values are recorded and interpreted. Glucose is the primary energy source of the body’s cells (including the brain) and hence the relatively constant level of glucose must be maintained in the blood. Normally after a meal, blood glucose rises and so the hormone insulin (secreted from the pancreas), helps transport glucose to the body’s cells where it is used as a source of energy (ATP produced by glycolysis and Kreb’s cycle). Diabetes is a disease resulting from an imbalance between glucose and insulin. Type-1 diabetes results when the body is not able to produce insulin to control blood glucose levels (auto-antibodies that destroy the beta cells of the pancreas) and type-2 diabetes results from a combination of insulin resistance (reduced sensitivity of insulin against blood glucose compared to a normal person’s response) and a relative decline in insulin production. Other types of diabetes include gestational diabetes (the condition restores back to normal after the pregnancy period), juvenile diabetes, etc. The test result of the glucose tolerance test is represented as a blood glucose chart that shows a person’s blood sugar levels – including before (fasting) and after meals (post-prandial). It helps a person with glucose management to maintain within normal range or in the prognosis of patients with diabetes treatment plans. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test(OGTT) is the gold standard for diabetes type 2 and is also useful in pre-diabetes, gestational diabetes, insulin resistance, impaired beta-cell function, disorders of carbohydrate metabolism (carbohydrate metabolism), and risk of developing diabetes prior to pregnancy or in high-risk cases of developing diabetes during pregnancies, etc. It identifies the abnormalities in the way the patient’s body handles glucose after a test dose of glucose (75 / 100 Grams) is administered. The patient is fasted for about eight hours before the test or preferably fasted overnight and the test schedule is performed in the early morning hours. A blood specimen is drawn to monitor the glucose levels in different time intervals (30 minutes, 1 hour, 1 ½ Hour’s and 2 hours, etc). A graph is plotted against the time v/s blood glucose levels as the body system responds to the administered glucose load in OGTT. The test result is interpreted accordingly and diagnosis is made in the case of diabetic patients (impaired fasting glucose, impaired glucose tolerance, etc) with suitable treatment modalities. Causes are family history, obesity, high blood pressure, sedentary lifestyle, junk foods, old age, etc. Signs and symptoms are hyperglycemia, polyuria, polydipsia, and polyphagia, etc. Complications of untreated diabetes include morbidity and mortality rate (life expectancy), risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndrome, obesity, poly cystic ovarian disease (PCOD), damages in the thin and fine small arteries such as in the eyes, end-organ damages eg. eyes, kidneys, blood vessels, brain and heart, stress, foot problems, and other illnesses, etc. False-positive test results can arise in smokers, consuming coffee (caffeine-based products), and patients on certain medications like corticosteroids, diuretics (water pills), anti-depressants, etc. Other tests include Hb-A1c to monitor prognosis in patient’s compliance during diabetes treatment.
General instructions:
Sample Requirement: Specimen - Blood sample collected from the vein. Test Preparation: Post Lunch.
NOTE - Sample for specimen collections may vary based on the patient’s condition/cases according to the patient’s presenting complaints/signs or symptoms:
SPECIMEN REQUIREMENT (Special or Rare Cases) - As instructed and guided by Physician / Clinician / Pathologist / as per Laboratory’s requirements, according to procedures and protocols.
This Multi-Specialty Clinical Referral Laboratory RTDIAGNOSTICS provides precise and accurate tests with an extensive range of testing services to the medical centers to help in the diagnosis and identification of pathology in the test specimens for infectious diseases and also to evaluate the function of organ systems of the patient. It prevents further complications and helps to stabilize and restore health to near normalcy at the earliest without delay.



